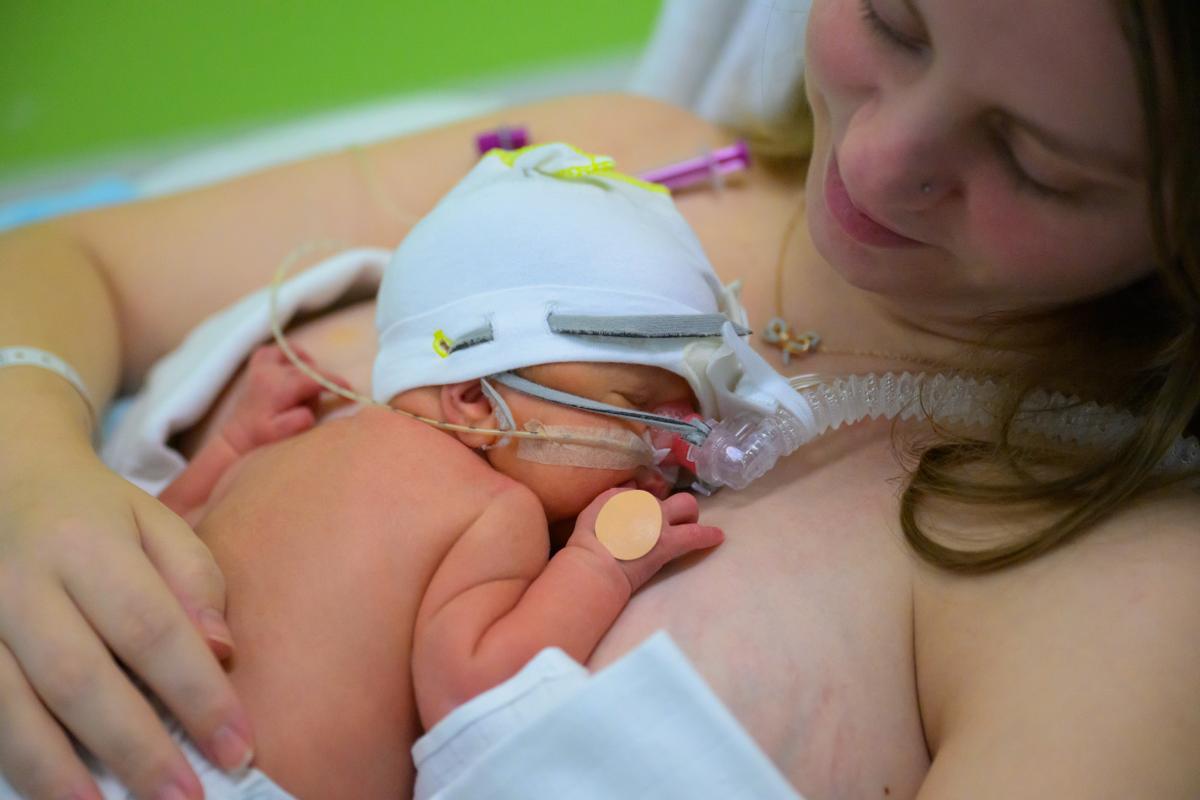
Donor milk offers better protection than formula
Donor breast milk contains several protective factors that help guard the baby against infections, particularly serious intestinal infections. These protective substances are present in much lower concentrations in formula.
Scientific studies have shown that using donor breast milk instead of formula helps prevent such infections in premature infants.
Where does donor breast milk come from?
We receive breast milk from healthy mothers who voluntarily donate their surplus milk. These mothers must first complete a questionnaire about their healthy lifestyle, similar to the process used for blood donation. Their blood is also screened for HIV, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C. They are given instructions on how to express and store the milk hygienically. The donor’s identity is always treated confidentially and is never shared with the parents of the baby receiving the milk.
When all questionnaire answers and test results are reassuring, the milk is accepted for donation. Samples are taken to check for any pathogens. The milk is deep-frozen and pasteurised before being given to babies, which eliminates any potential harmful bacteria and minimises the risk of infection.
Read more about donating breast milk.
Are there any risks of complications?
The risk of complications is very low, as the donors' health is carefully screened and the donor milk is stored safely. While the risk of infection can never be completely ruled out, it remains minimal, and the benefits of using donor milk far outweigh this small risk.
What if I have religious objections to donor breast milk?
Certain religions and traditions have specific rules regarding the use of donor breast milk. If you have concerns about this, speak to your doctor.